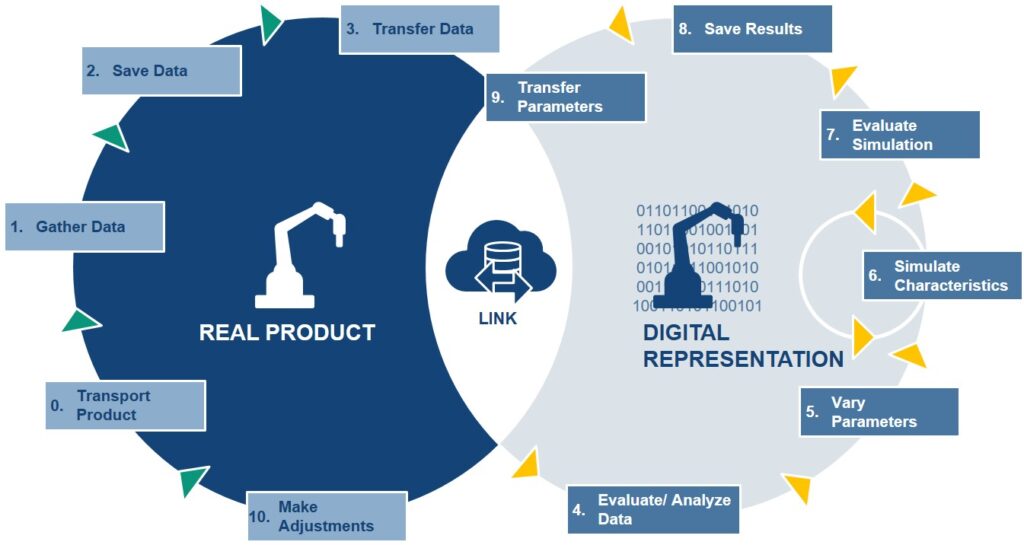
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, generative artificial intelligence (AI) stands out as a transformative force. As industries across the board embrace the potential of AI, organizations from municipalities to oil and gas companies are discovering how this cutting-edge technology can address their unique challenges and drive innovation.
Generative AI, a subset of artificial intelligence that involves machines creating new content, has been making waves in diverse sectors. In today’s post, we delve into how generative AI is reshaping the way municipalities operate and how it’s bringing about groundbreaking changes in the oil and gas industry.
The Evolving Landscape of Municipalities
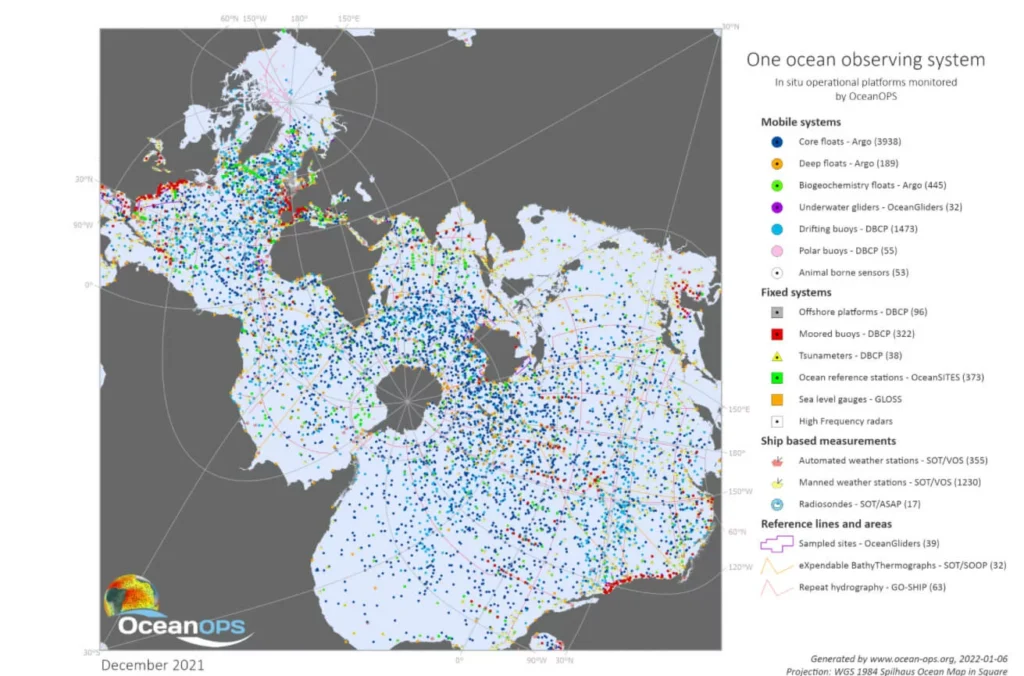
Municipalities face a myriad of challenges, from urban planning to citizen services. Generative AI offers a promising solution by optimizing city operations and enhancing infrastructure planning. By analyzing vast datasets, generative AI algorithms can predict traffic patterns, optimize public transportation routes, and even contribute to effective disaster response planning. The result is a more streamlined and efficient urban environment that improves the quality of life for residents.
Innovations in Oil and Gas with Generative AI
The oil and gas industry, known for its complex processes, is undergoing a revolution with the integration of generative AI. Reservoir management, exploration, and production optimization are areas where AI algorithms can make a significant impact. By analyzing geological data and predicting potential reserves, generative AI assists companies in making informed decisions, reducing environmental impact, and enhancing overall safety protocols.

Real-world Applications
Real-world applications of generative AI in municipalities and oil and gas companies are already yielding impressive results. In Barcelona, Spain, for example, generative AI is being used to optimize waste collection routes, leading to a reduction in fuel consumption and emissions. In the oil and gas sector, companies like ExxonMobil are employing AI-driven technologies to improve drilling efficiency and reduce operational costs.

Addressing Concerns and Challenges
As with any emerging technology, concerns arise regarding data privacy, ethics, and potential job displacement. It is crucial for companies and municipalities to address these challenges responsibly. Striking a balance between innovation and ethical considerations ensures that generative AI is implemented in a way that benefits both industries and society as a whole.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, the future of generative AI holds even more promise. Ongoing research and developments indicate that the technology will continue to evolve, bringing about new and improved applications for municipalities and oil and gas companies. As AI becomes more sophisticated, its ability to solve complex problems and drive innovation will only increase.

Conclusion
The integration of generative AI is reshaping the landscapes of municipalities and oil and gas companies. From optimizing city operations to revolutionizing resource extraction processes, the potential benefits are vast. As these industries continue to embrace AI, it is essential to stay informed about the latest developments and explore how your company can leverage generative AI for a sustainable and efficient future. Stay ahead of the curve by exploring how generative AI can benefit your organizations! Learn more AI implementation, and discover the transformative power of generative artificial intelligence.